Simplified PHP for beginers, makes projects fatser with Database management, Localizations, Admin panel, Extensions, File management, Routing and many more.

Clone the repository preferrabely into an htdocs folder where you can serve a php project
git clone https://github.com/matnex-mix/sphp.gitEdit config.json and add a database configuration follow the format there already
...
"DB": [{
"name": "<DB_NAME>",
"user": "<DB_USER>",
"pass": "<DB_PASS>",
"host": "<DB_HOST>"
}],
...Save and view your app in the browser http://localhost/sphp
Add a json file in the migrations folder let's say migrations/add_users_table.json and add the following migration commands in the json file
{
"create": {
"users": {
"id": {
"type": "int",
"primary": true,
"auto_increment": true
},
"name": {
"type": "varchar",
"length": 50
},
"created_at": {
"type": "timestamp",
"length": 1
}
}
}
}save then visit APP_URL/migrate, you should see a sql breakdown of the migration
Edit the migrations/seeder.php file and add the below code
<?php
...
DB::seeder('users', array(
'name' => Factory::mix('a', 5),
'created_at' => Data::runner(function(){
return Date('Y-m-d H:i:s');
}),
])
->repeat(10);then visit APP_URL/migrate in your browser. You should see 10 different rows in your table, MAGIC right?
An example of this is available when you visit APP_URL/en and APP_URL/in, you should check the title bar and see the differences. Open the language file langs/english.php or langs/hindi.php and add the below code
english.php
<?php
...
L::set('hello_world', 'Hello World!');hindi.php
<?php
...
L::set('hello_world', 'Namaste World!');then in your pages/index.php file add
<?php
...
die( L::get('hello_world') );now visit APP_URL/en and APP_URL/in, to check the difference
Basically, all urls correspond to a php file in /pages folder, take for example i visited APP_URL/test_page, the framework would lookup the file pages/test_page.php or pages/test_page/index.php then fallbacks to pages/404.php if it couldn't find any of the files. Create 2 new files in /pages folder
404.phpadd<?php echo "<h2>THIS IS 404 PAGE</h2>"; ?>new_page.phpadd<?php echo "<h2>THIS IS A NEW PAGE</h2>"; ?>
Visit APP_URL/new_page and APP_URL/eva in your browser to see the result
Models are classes that makes quering database tables easier representing them by a PHP object for instance:
-----------------------------------
| id | name | created_at |
-----------------------------------
| 1 | mix | 2020-08-31 11:34:00 |
-----------------------------------
would become:
stdClass({
->id = 1
->name = 'mix'
->created_at = '2020-08-31 11:34:00'
})to use: add a new file models/users.php then add below code
<?php
class Users extends Model {
// Set Toggle Showing Sql Query Errors
protected $show_errors = true;
// Set Target Table to `users`
protected $table_name = 'users';
}to test: edit pages/index.php and add
<?php
...
Model::load('users');
print_r( Users::get()
->order('id', 'DESC')
->show() );SPHP has its own way of automatically passing data to html pages making work easier and faster. Create a new file say static/templates/test.html and add:
<h2>Title: {( @title )}</h2>
<ul>
{( for contents )}
<li>{( @this )}</li>
{( endfor )}
</ul>and add the below code in pages/index.php:
<?php
...
echo Template::parse('test', array(
'title' => 'Testing SPHP templates',
'contents' => [
'Item 1',
'Item 2',
'Item 3'
]
));For database management, a substitute for MySQL queries. It has methods for the basic common sql operations:
<?php
...
# Insert into a database
var_dump(
DB::insert('users', array(
'name' => 'Matnex Mix',
'created_at' => Date('Y-m-d H:i:s'),
))
);
# Retrieve data example
# The below code uses some tables which have not been defined, note that this is just and example
var_dump(
DB::table('history')
->innerJoin(DB::table('users')
->where( '>id', 0 ))
->on([
'history.user' => 'users.id'
])
->where( '*history.summary', '%' )
->braces('||')
->braces('&&')
->where( 'history.id', 20 )
->where( 'history.id', 21 )
->close()
->where( '+*history.time', '2020-08-02' )
->close()
->show()
);
# Update table
var_dump(
DB::update('users', array(
'name' => 'New name'
))
->where('id', 1)
->run()
);
# Delete data from table
var_dump(
DB::delete('users')
->where('id', 1)
->run()
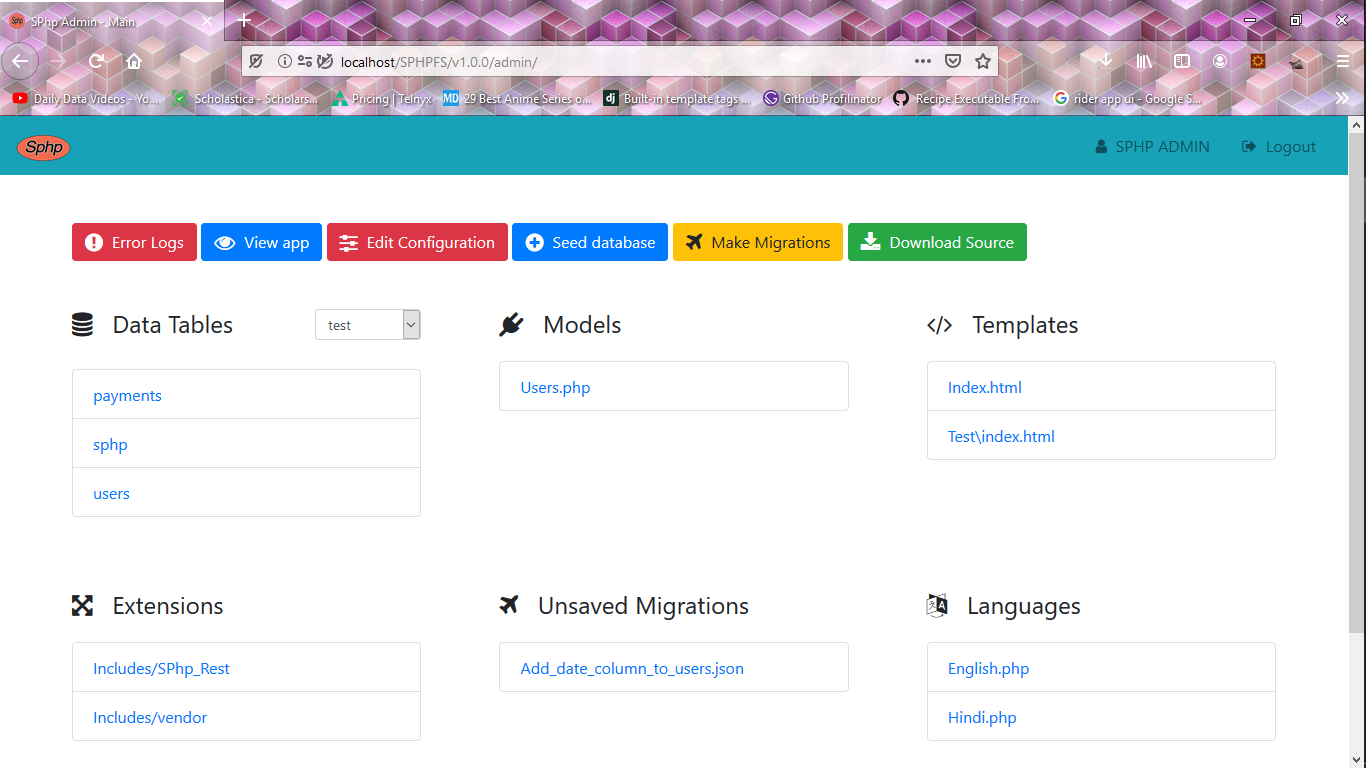
);Manage your app from within your app, sphp-admin can manage database, show errors and edit files. Visit APP_URL/admin and login with
- username: sphp-admin
- password: sphp_admin
- Write real documentation
- Add more template filters
We're glady accepting contribution and issues, create an issue if you have one or add a pull request to contribute to this project.