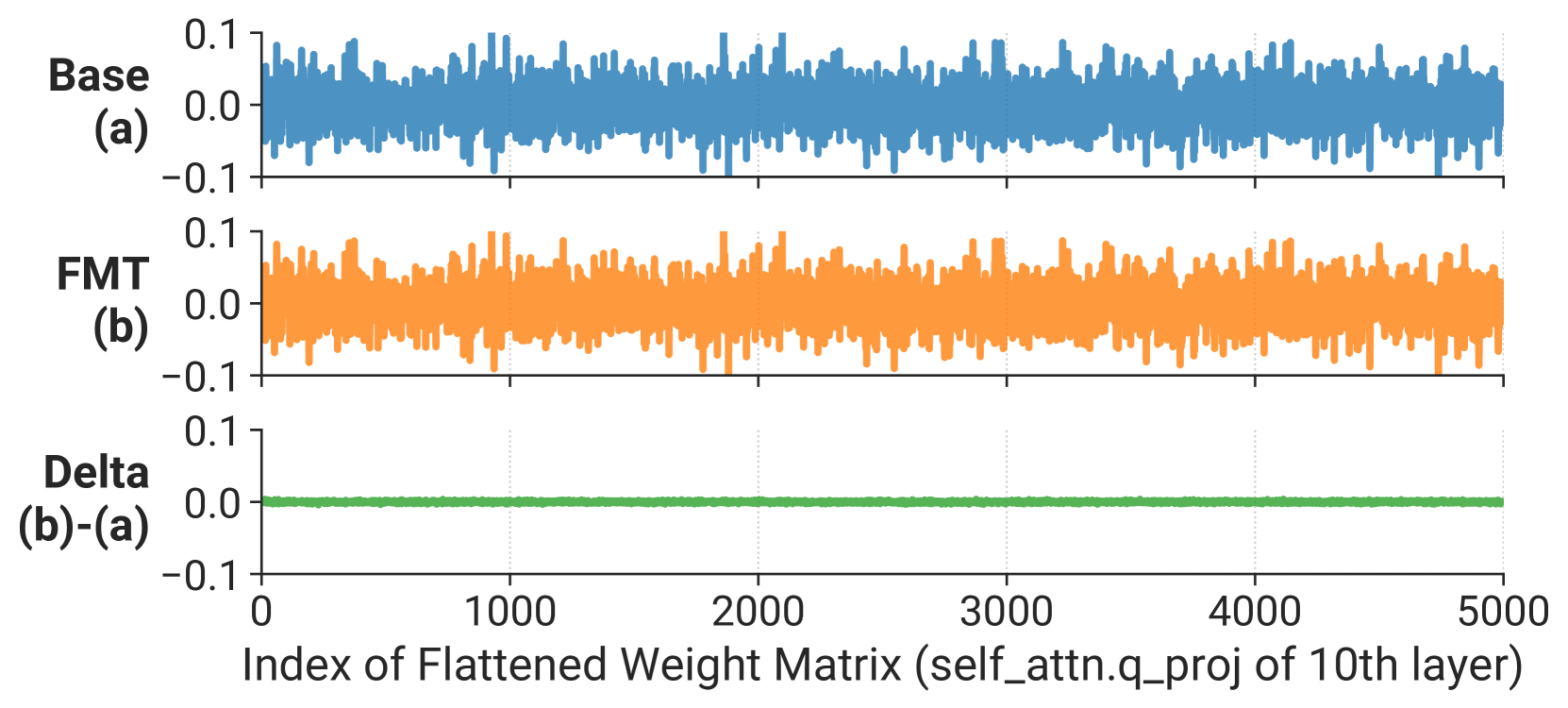
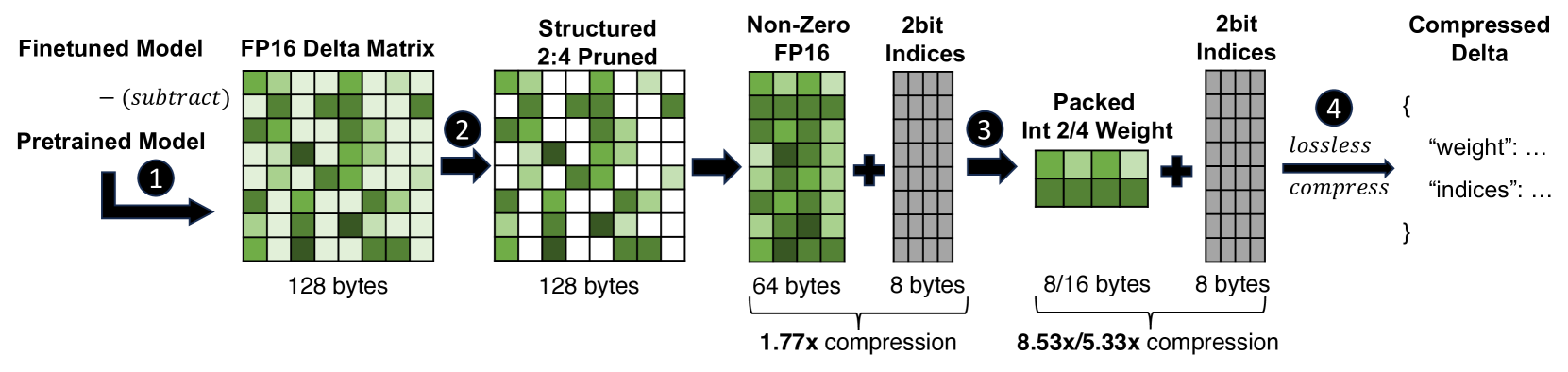
DeltaZip is a system for compressing and serving full-parameter fine-tuned LLMs.
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) greatly improves model quality for downstream tasks. However, serving many fine-tuned LLMs concurrently is challenging due to the sporadic, bursty, and varying request patterns of different LLMs. To bridge this gap, we present DeltaZip, an LLM serving system that efficiently serves multiple full-parameter fine-tuned models concurrently by aggressively compressing model deltas by up to 10x while maintaining high model quality. The key insight behind this design is that fine-tuning results in small-magnitude changes to the pre-trained model. By co-designing the serving system with the compression algorithm, DeltaZip achieves 2x to 12x improvement in throughput compared to the state-of-the-art systems.
We observe that the weight updates from the pre-trained model to the fine-tuned model are small in magnitude, and smoothly distributed.
Inspired by this motivation, we compose an aggressive compression pipeline that includes both structured sparsity and quantization. The pipeline consists of the following steps:
This pipeline is designed to be efficient in both compression ratio and inference speed: 1) We employ structured sparsity, which is supported by recent hardware accelerators, such as post-ampere NVIDIA GPUs. 2) By compression, we reduce the data movement needed from GPU HBM to the compute unit, which is the main bottleneck in LLM inference.
deltazip/
├── README.md # Project documentation
├── LICENSE # Apache 2.0 license
├── cli/ # Command line utils
├── deltazip/ # Core compression utils
├── serving/ # serving systems (based on vllm)
├── scripts/ # Experiment and evaluation scripts
│ ├── env.sh # Environment configuration
│ ├── 1_compress_7b.sh # Compress 7B models
│ ├── 1.1_test_generate.sh # Test text generation
│ ├── 2_eval_quality*.sh # Model quality evaluation scripts
│ ├── 3*_serve*.sh # Performance evaluation scripts
│ ├── 4_cleanup.sh # Environment cleanup
│ ├── helpers/ # Helper scripts
│ │ ├── aggregate_accuracy.py
│ │ ├── aggregate_perf.py
│ │ └── bench.py # Benchmarking tool
│ └── workload/ # Benchmark workloads
│ └── azure.ar=0.5.jsonl # Sample workload
└── tests/ # Unit and integration tests
├── test_compress.py
└── test_serve.py
We provide a pre-built docker image for DeltaZip.
docker pull ghcr.io/xiaozheyao/deltazip:0.0.1Before executing the bash commands below, please make sure you have read the scripts and have environments set up correctly (see scripts/env.sh).
bash scripts/1_compress_7b.shThis command compresses the Vicuna-1.5 7B model using DeltaZip down to 2 bit precision and 50% sparsity. The compressed model is stored in the $WORKDIR/compressed_models directory.
This command takes around ~20 to ~30 minutes to run.
Note: the above command prints some debugging information, such as
...
[info] model.model.layers.18.post_attention_layernorm.weight is not saved
...
and this information is expected (as we don't store the layernorm.weight anyway).
bash scripts/1.1_test_generate.shThis should return something like:
...
Namespace(target_model='/local/compressed_models/lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs', prompt='Who is Alan Turing?')
BaseCompressionConfig(bits=2, sparsity=0.5, prunen=2, prunem=4, group_size=-1, group_rows=-1, block_size=128, damp_percent=0.01, desc_act=False, sym=True, true_sequential=True, lossless='gdeflate', dtype='fp16')
Loading base model meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf...
Loading checkpoint shards: 100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:00<00:00, 3.49it/s]
[warn] default chat template is not set in the tokenizer.
Generated:
Alan Turing (1912-1954) was a British mathematician, computer scientist, and logician who is widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in the development of computer science and artificial intelligence.
During World War II, Turing worked at the Government Code and Cypher School, where he made significant cont
ributions to the breaking of the Enigma code, which helped the Allies to decipher German communications and gain a strategic advantage in the war.
After the war, Turing turned his attention to the field of computer science and proposed the
As you can see, this command generates a valid response from the compressed model.
We then evaulate the accuracy of the compressed model and compare it with the original model.
To evaluate the accuracy of the compressed model, run the following command:
bash scripts/2_eval_quality_compressed.shNote: we reuse the lm-eval-harness to evaluate the quality of the model, to avoid any risks of writing quality evaluation ourselves.
To evaluate the accuracy of the original model, run the following command:
bash scripts/2_eval_quality_original.shThe above commands will print the accuracy of the model (depending on which command you run, scripts/2_eval_quality_compressed.sh prints the quality of the compressed model, and scripts/2_eval_quality_original.sh prints the original model) in a table format:
| Tasks |Version|Filter|n-shot| Metric | | Value | |Stderr|
|--------------|------:|------|-----:|-----------|---|------:|---|-----:|
|boolq | 2|none | 0|acc |↑ | 0.8162|± |0.0068|
|logiqa | 1|none | 0|acc |↑ | 0.2842|± |0.0177|
| | |none | 0|acc_norm |↑ | 0.3195|± |0.0183|
|truthfulqa_gen| 3|none | 0|bleu_acc |↑ | 0.5104|± |0.0175|
| | |none | 0|bleu_diff |↑ | 7.7702|± |0.9598|
| | |none | 0|bleu_max |↑ |29.6408|± |0.8426|
| | |none | 0|rouge1_acc |↑ | 0.5153|± |0.0175|
| | |none | 0|rouge1_diff|↑ |11.0801|± |1.3235|
| | |none | 0|rouge1_max |↑ |55.4865|± |0.9114|
| | |none | 0|rouge2_acc |↑ | 0.4688|± |0.0175|
| | |none | 0|rouge2_diff|↑ |10.4691|± |1.4551|
| | |none | 0|rouge2_max |↑ |42.0726|± |1.0961|
| | |none | 0|rougeL_acc |↑ | 0.5092|± |0.0175|
| | |none | 0|rougeL_diff|↑ |11.2277|± |1.3243|
| | |none | 0|rougeL_max |↑ |52.8604|± |0.9439|
|truthfulqa_mc1| 2|none | 0|acc |↑ | 0.3305|± |0.0165|
|truthfulqa_mc2| 2|none | 0|acc |↑ | 0.4966|± |0.0155|(Note we take average accuracy for truthfulqa_mc1 and truthfulqa_mc2)
The script will also write the accuracy to $WORKDIR/eval_results/lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs directory and $WORKDIR/eval_results/lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 directory respectively.
The above commands should take around 1 hour to run.
We provide a helper script to compare the accuracy of the original and compressed models, as well as the compression ratio:
python scripts/helpers/aggregate_accuracy.py --compressed-model $WORKDIR/compressed_models/lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs --full-model lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 --accuracy-dir $WORKDIR/eval_results(Note: the script requires huggingface-hub, which you can install with pip install huggingface-hub)
This should return:
Original model size: 12853.13MB
[DeltaZip] compressed model size: 1303.79MB
Compression ratio: 9.86x
+------------------------------------+------------+----------+
| model | task | accuracy |
+------------------------------------+------------+----------+
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs | boolq | 81.62% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs | logiqa | 28.42% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs | truthfulqa | 41.36% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 | boolq | 80.92% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 | logiqa | 27.65% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 | truthfulqa | 41.64% |
+------------------------------------+------------+----------+and you should expect the two models to have similar accuracy on these tasks. Here lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs refers to the model compressed using deltazip with 2-bit precision and 50% sparsity, and lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 refers to the original model.
In order to compress and evaluate the model with baseline approaches, we provide a script to do so with two baselines: SparseGPT and AWQ.
bash scripts/2.1_compress_baselines.shbash scripts/2.2_eval_baselines.shYou can summarize the results with the following command:
python scripts/helpers/aggregate_accuracy.py --compressed-model $WORKDIR/compressed_models/lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs --full-model lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 --accuracy-dir $WORKDIR/eval_results --sparsegpt-model $WORKDIR/sparsegpt_models/lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b_2n4m_128bs --awq-model $WORKDIR/awq_models/awq.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128gThe above command should return:
Original model size: 12853.13MB
[DeltaZip] compressed model size: 1303.79MB
[DeltaZip] Compression ratio: 9.86x
[SparseGPT] model size: 2445.54MB
[SparseGPT] Compression ratio: 5.26x
[AWQ] model size: 3713.14MB
[AWQ] Compression ratio: 3.46x
+---------------------------------------+------------+----------+
| model | task | accuracy |
+---------------------------------------+------------+----------+
| awq.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g | boolq | 81.22% |
| awq.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g | logiqa | 27.34% |
| awq.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g | truthfulqa | 42.24% |
| sparsegpt.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g | boolq | 67.95% |
| sparsegpt.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g | logiqa | 23.96% |
| sparsegpt.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g | truthfulqa | 35.29% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs | boolq | 81.62% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs | logiqa | 28.42% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs | truthfulqa | 41.36% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 | boolq | 80.92% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 | logiqa | 27.65% |
| lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 | truthfulqa | 41.64% |
+---------------------------------------+------------+----------+(Here lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.2b_2n4m_128bs refers to the model compressed using deltazip with 2-bit precision and 50% sparsity, and lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5 refers to the original model. awq.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g refers to the model compressed using AWQ with 4-bit precision, and sparsegpt.lmsys.vicuna-7b-v1.5.4b128g refers to the model compressed using SparseGPT with 4-bit precision and 50% sparsity.)
(Note: Due to some randomness in the compression process, the exact accuracy numbers and compression ratio may vary slightly. But in general we expect the compression ratio of DeltaZip to be around 10x, AWQ to be around 3.5x and SparseGPT to be around 5x. The accuracy of DeltaZip and AWQ should be similar to the original model, while the accuracy of SparseGPT should be lower.)
So far we finished the accuracy evaluation.
Note 1: In the paper, we run our experiments on a high-performance HPC cluster. Since we cannot grant access to the HPC cluster, we provide a script to evaluate the serving performance on a single machine on the Cloud.
[You can skip this step if the deltas are already prepared on the system (which should be already), please check the $WORKDIR/models/deltas and $WORKDIR/models/full directory] In order to evaluate the serving performance of our system, we first need to compress the 13b model, prepare the delta weights and create multiple copies.
bash scripts/3_compress_13b.sh
bash scripts/3_prepare_delta.shNote 2: We pre-partition the model weights into the tensor-parallel shards. If you change the tensor-parallel degree, you need to re-partition the model weights. By default, we set tensor parallel degree to be 4.
Note 3: If you are running on your own instance, and do not have enough GPU memory to serve the model, please consider using a smaller model (e.g., 7B model) for evaluation.
The above command will create the delta weights and store them in the $WORKDIR/models/deltas directory.
We have already copied the full model weights to $WORKDIR/models/full. If you want to prepare the full model weights you self, you can run the following command:
python3 scripts/helpers/prepare_full_models.py --model lmsys/vicuna-13b-v1.5 --target $WORKDIR/models/full --num-copies 24bash scripts/3.1_serve_delta.shIn another terminal, run the following command to start the client:
python3 scripts/helpers/bench.py --workload scripts/workload/azure.ar=0.5.jsonl --base-model meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-hf --output $WORKDIR/resultsOnce the client finishes, you can stop the server with Ctrl+C. Please also check if the docker container exits properly by docker ps. If it is still running, please execute docker stop [container ID].
bash scripts/3.2_serve_full.shIn another terminal, run the following command to start the client:
python3 scripts/helpers/bench.py --workload scripts/workload/azure.ar=0.5.jsonl --base-model meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-hf --output $WORKDIR/resultsOnce the client finishes, you can stop the server with Ctrl+C. Please also check if the docker container exits properly by docker ps. If it is still running, please execute docker stop [container ID].
You can then aggregate the results with the following command:
python scripts/helpers/aggregate_perf.py --dir $WORKDIR/resultsThis should return the key metrics of the serving performance as below:
+--------------+-------------+----------+------------+
| sysname | avg_latency | avg_ttft | throughput |
+--------------+-------------+----------+------------+
| Baseline (1) | 169.49 | 153.66 | 0.0537 |
| DeltaZip (6) | 34.86 | 3.52 | 0.1782 |
+--------------+-------------+----------+------------+
Note: the performance numbers may vary depending on the exact machine you are running the evaluation on. The following numbers are collected on a cloud machine with 4xA100 GPUs and around 100MB/s disk bandwidth. In general, we expect DeltaZip to have lower latency and higher throughput compared to the baseline.
+--------------+-------------+----------+------------+
| sysname | avg_latency | avg_ttft | throughput |
+--------------+-------------+----------+------------+
| DeltaZip (8) | 236.90 | 142.57 | 0.1217 |
| Baseline (6) | 2410.80 | 1924.14 | 0.0143 |
+--------------+-------------+----------+------------+bash scripts/4_cleanup.shHeavily inspired by
- IST-DASLab/Sparse-Marlin
- IST-DASLab/gptq
- IST-DASLab/sparsegpt
- PanQiWei/AutoGPTQ
- qwopqwop200/GPTQ-for-LLaMa
- vllm-project/vllm
If you found this code useful, please cite our paper:
@article{yao2023deltazip,
title={DeltaZip: Multi-Tenant Language Model Serving via Delta Compression},
author={Yao, Xiaozhe and Klimovic, Ana},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.05215},
year={2023}
}
@inproceedings{
isik2023gptzip,
title={{GPT}-Zip: Deep Compression of Finetuned Large Language Models},
author={Berivan Isik and Hermann Kumbong and Wanyi Ning and Xiaozhe Yao and Sanmi Koyejo and Ce Zhang},
booktitle={Workshop on Efficient Systems for Foundation Models @ ICML2023},
year={2023},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=hO0c2tG2xL}
}